Variable temperature in situ TEM mapping of the thermodynamically stable element distribution in bimetallic Pt–Rh nanoparticles
In-situ TEM experiments shows that the tendency for elemental mixing- or segregation to occur in Pt–Rh nanoparticles depends on the nanoparticle size and temperature. The smaller nanoparticles (≲13 nm) are stable in the solid solution configuration over the entire studied temperature range. Larger nanoparticles (≳13 nm) tends to segregate when cooled to room temperature. The results are of importance to understand the thermodynamics of this specific Pt–Rh nanoparticle system and it add value towards applications like catalysis, whereof e.g. supported Pt–Rh nanoparticles are attractive candidates for NH3 slip abatement processes.
Nanoscale Adv. 5, 5286 (2023).
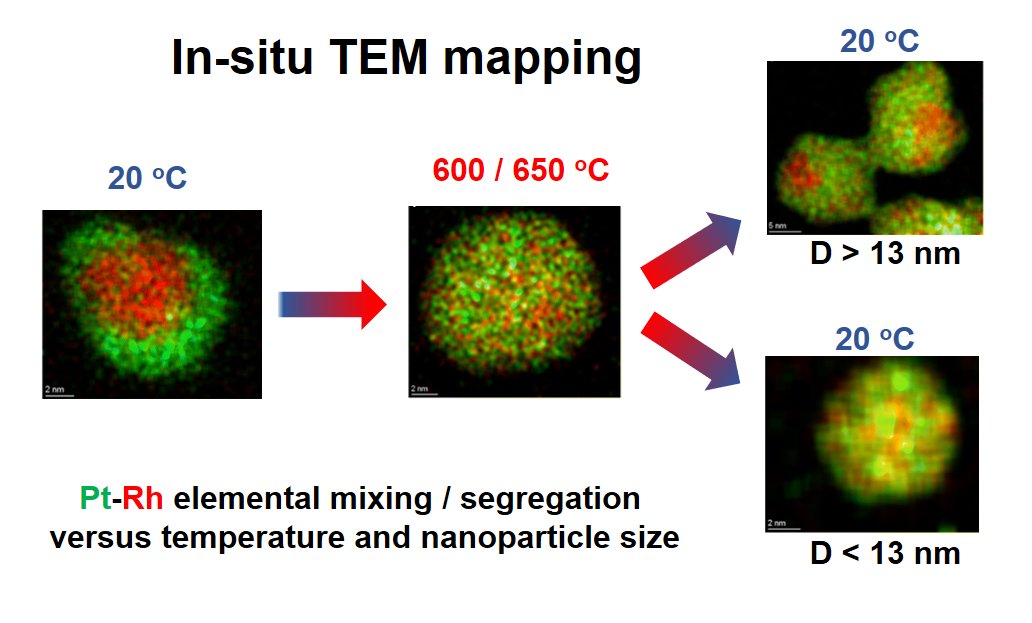
In-situ TEM experiments shows that the tendency for elemental mixing- or segregation to occur in Pt–Rh nanoparticles depends on the nanoparticle size and temperature. The smaller nanoparticles (≲13 nm) are stable in the solid solution configuration over the entire studied temperature range. Larger nanoparticles (≳13 nm) tends to segregate when cooled to room temperature. The results are of importance to understand the thermodynamics of this specific Pt–Rh nanoparticle system and it add value towards applications like catalysis, whereof e.g. supported Pt–Rh nanoparticles are attractive candidates for NH3 slip abatement processes.
Tags:
TEM,
Nanoteknologi,
Nanotechnology,
Nafuma
By
Martin Jensen,
Walace Kierulf-Vieira,
Patricia J. Kooyman,
Anja O. Sjåstad
Published Sep. 25, 2023 2:42 PM
- Last modified Nov. 28, 2023 10:35 AM
