Services
- Consultation, feedback and sample delivery (bernd.thiede@ibv.uio.no)
- Protein separation and staining
- Lysis and protein precipitation
- In-gel and in-solution protein digestion and sample clean-up
- Phosphopeptide enrichment
- LC-MS analysis
- Protein quantification (LFQ)
- Mascot/Scaffold and PEAKS data analysis
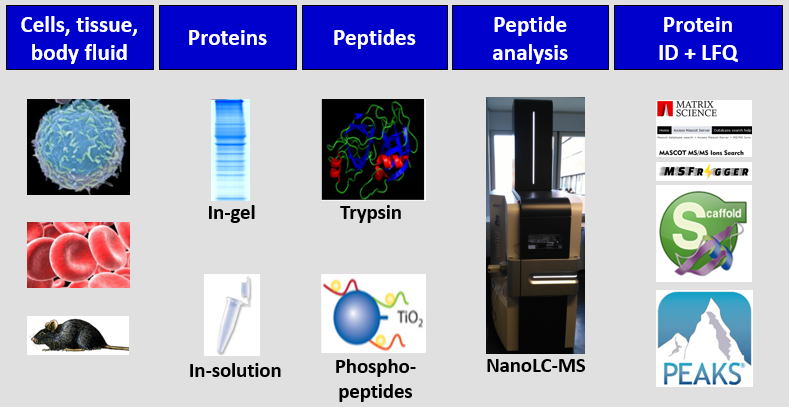
Techniques
-
SDS-PAGE: Protein separation and staining in preparation for further analysis. Either complete lanes or selected bands of interest can be analyzed. It can be offered in two different sizes (6 cm or 10 cm). Staining with Coomassie G-250 is ideally suited in combination with mass spectrometry.
- Lysis and protein precipitation: For in-solution digests, proteins must be extracted from cells and tissues and purified by precipitation to remove contaminants (e.g., buffers, detergents etc.) which would disturb digestion.
- In-gel and in-solution digestion of proteins: Protein identification is usually done after generation of tryptic peptides. Trypsin is ideally suited to mass spectrometry, because of the average size of the peptides, charge state, and specificity of the enzyme. For in-solution digestion, reductive alkylation is performed before using trypsin for unfolding and denaturation of the proteins in 6M urea. We purify our peptide samples with micro-SPE C18-tips to avoid problems with sensitivity and LC and MS instrumentation.
- Phosphopeptide enrichment: For large-scale phosphoproteomics experiments, large starting material is required (> 1 mg). After digestion of the proteins with trypsin, the phosphopeptides are enriched with TiO2 beads.
- LC-MS (TimsTOF Pro): Protein identification. Complex samples must be further purified by nanoLC (200-300 nl/min) before analysis by MS. An UHPLC is directly connected to the mass spectrometers and allows fast, highly sensitive and robust analysis with high mass accuracy. Usually, the samples derive from SDS-PAGE gel bands or after in-solution digestion. LC gradient times are dependent on the complexity of the sample.
- Protein identification: The data are usually searched using the mass search program Mascot and provided as Scaffold file or by using PEAKS Studio. Scaffold and PEAKS viewer can be freely downloaded on any PC.
- Quantitative data analysis: Label free quantification (LFQ) is a frequently used method for MS-based relative quantitative proteome analysis. PEAKS Studio is a software program that allows statistically robust identification and quantification of proteins.
